How to Optimize Content for SEO: A Step-by-Step Checklist
You publish content, but it sits on page three of Google. Your competitors with similar topics rank higher. You wonder if you missed something in your keyword research, or maybe the content just needs better formatting. The truth is simpler: knowing how to optimize content for SEO requires more than guessing at what works. It demands a repeatable system that covers everything from search intent to technical elements.
Content optimization is not about stuffing keywords or following outdated tactics. It is a structured process that aligns your content with what Google rewards and what readers actually need. When done right, optimization takes existing content and transforms it into a ranking asset that drives consistent organic traffic.
This guide walks you through six clear steps to optimize any piece of content for better search performance. You will learn how to validate search intent, map keywords strategically, improve readability, fix technical elements, build authority signals, and maintain your rankings over time. Each step includes actionable tactics you can apply immediately to your content.
What content optimization means in 2026
Content optimization in 2026 goes beyond keyword placement and meta tags. Google's algorithms now prioritize user satisfaction signals, including how long visitors stay on your page, whether they return to search results immediately, and if they engage with your content. You need to understand that optimization is not a one-time task but a continuous improvement process that adapts to both algorithm updates and changing user behavior.
The definition of optimized content has expanded significantly. Your content must now satisfy multiple ranking systems simultaneously: traditional search engines, AI chat platforms like ChatGPT and Gemini, and voice assistants. Each platform evaluates content differently, but they all reward the same core principles of clarity, authority, and usefulness. When you learn how to optimize content for SEO today, you are building content that performs across the entire digital ecosystem.
Focus on user signals and experience
Google measures user satisfaction through behavioral signals that your content generates. If visitors click your result and immediately return to search, Google interprets this as a poor match for that query. Your optimization efforts must address this by ensuring content delivers exactly what the search intent promises. This means your introduction must confirm the topic immediately, your structure must allow easy scanning, and your answers must appear quickly without forcing readers to scroll through filler content.
You should also consider engagement metrics like time on page and scroll depth. Google's algorithms have become sophisticated at detecting when content genuinely helps users versus when it simply exists to rank. Create content that encourages natural engagement by including relevant examples, breaking complex ideas into digestible sections, and anticipating follow-up questions your readers will have.
Integration with AI platforms
AI chat platforms have changed how users discover content. When someone asks ChatGPT or Gemini a question, these systems pull from high-quality sources that demonstrate expertise. Your content must now be structured to serve as a citable reference for AI systems, which means clear attribution of facts, logical organization, and authoritative tone without unnecessary marketing language.
The way you format information matters for AI visibility. Use structured data where appropriate, write in clear declarative sentences, and organize information hierarchically. AI systems favor content that directly answers questions, provides specific data points, and includes proper context for claims.
Optimization in 2026 means creating content that serves both human readers and AI systems without compromising quality for either audience.
Technical excellence as baseline
Technical SEO is no longer optional for content optimization. Your pages must load in under 2.5 seconds, work flawlessly on mobile devices, and pass Core Web Vitals assessments. Google treats technical performance as a fundamental quality signal, not a bonus factor. If your content loads slowly or breaks on mobile, optimization efforts elsewhere will not overcome this handicap.
You also need proper HTML structure that helps both users and search engines understand your content hierarchy. This includes semantic heading tags (H1 through H3), descriptive alt text for images, and clean URL structures. Search engines have moved past forgiving messy code, and your content must meet these baseline technical standards to compete for rankings in 2026.
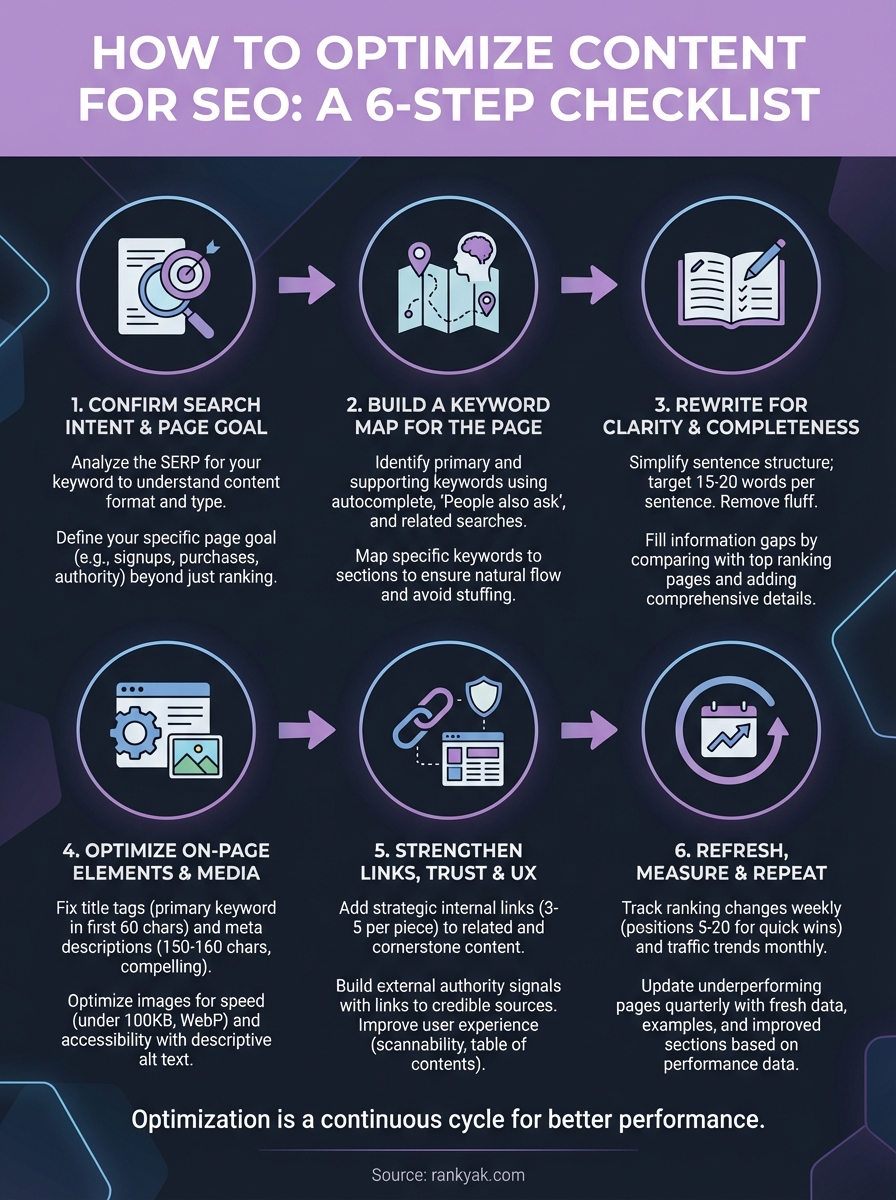
Step 1. Confirm search intent and page goal
Before you change a single word or add any keywords, you must verify that your content matches what searchers actually want. This step prevents the most common optimization mistake: creating technically perfect content that answers the wrong question. You need to examine the current search results for your target keyword and confirm that your content type, format, and depth align with what Google already ranks.
Analyze the SERP for your keyword
Open an incognito browser window and search for your exact target keyword. Look at the top five results and identify patterns in content type. If Google shows product comparison pages for your keyword but you wrote a beginner's guide, you have a search intent mismatch. Your content will struggle to rank regardless of how well you optimize it.

Note the content format that dominates results. Check whether Google favors lists, step-by-step tutorials, long-form guides, or video content. If four of the top five results use a specific format, that format matches search intent. You should adapt your content to reflect this pattern rather than fight against it. Document these observations before moving to the next step.
When your content format matches what Google already ranks, you remove a major barrier to visibility.
Define your specific page goal
Every optimized page needs a clear conversion goal beyond just ranking. Decide whether this page should generate email signups, drive product purchases, build topical authority, or support another page that converts. Your goal determines which calls-to-action you include and how you structure your content flow.
Write down your page goal in one sentence before continuing. An example goal might be: "This page will rank for 'how to optimize content for seo' and drive readers to sign up for our SEO automation trial." This clarity helps you make better decisions about content depth, internal linking, and conversion elements. Your optimization choices should support this goal instead of working against it.
Check that your current content actually delivers on the promise made in your title and meta description. If your title promises a comprehensive checklist but your content only covers three basic tips, you create a satisfaction gap that hurts rankings. Match your content depth to user expectations before optimizing other elements.
Step 2. Build a keyword map for the page
A keyword map is your strategic plan for which terms appear where in your content. You cannot optimize effectively by randomly sprinkling keywords throughout your page. Instead, you need a deliberate approach that assigns specific keywords to specific sections based on search volume, relevance, and natural content flow. This step transforms generic content into a targeted asset that captures multiple search queries without keyword stuffing.
Identify primary and supporting keywords
Start with your main target keyword and find related terms that searchers actually use. Open Google and type your main keyword, then note the autocomplete suggestions that appear. Scroll to the bottom of search results and review the "People also ask" section and related searches. These reveal the actual questions and variations people search when looking for information on your topic.
Your primary keyword should appear in your H1 heading, first paragraph, and at least one H2 heading. Supporting keywords belong in H3 headings, body paragraphs, and image alt text. For a page about how to optimize content for SEO, your supporting keywords might include "on-page optimization," "SEO checklist," "content ranking factors," and "keyword placement." Document these terms before writing or editing your content.
A well-structured keyword map increases your chances of ranking for dozens of related queries without creating separate pages for each variation.
Map keywords to specific sections
Create a simple table that assigns keywords to content sections. This prevents you from clustering too many keywords in one area while leaving other sections keyword-sparse. Your map ensures each section targets a specific search intent variation.
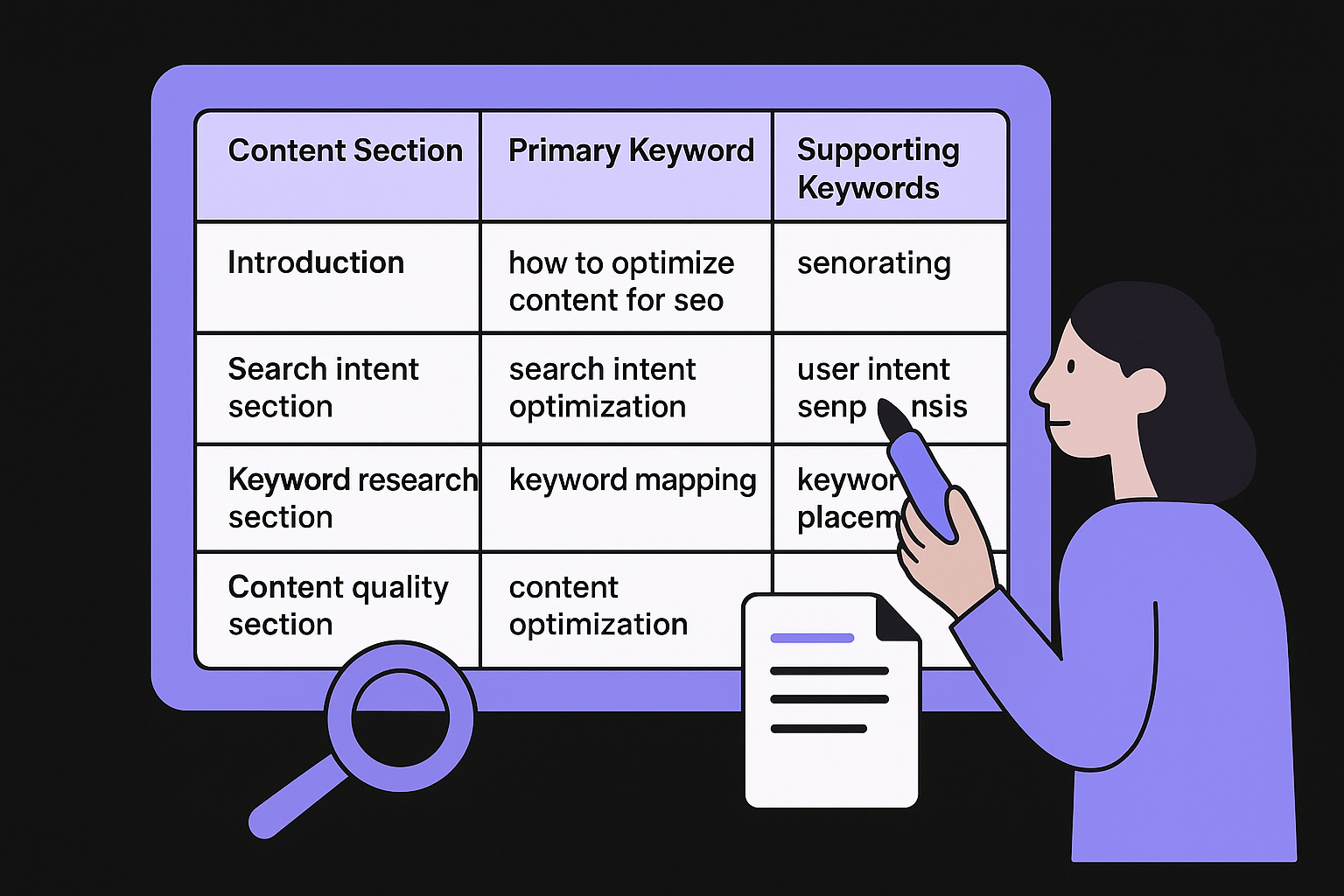
| Content Section | Primary Keyword | Supporting Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | how to optimize content for seo | content optimization, SEO strategy |
| Search intent section | search intent optimization | user intent, SERP analysis |
| Keyword research section | keyword mapping | keyword placement, LSI keywords |
| Content quality section | content optimization tips | readability, helpful content |
Use this structure to guide your writing or revision process. Each section should naturally incorporate its assigned keywords without forcing them into sentences where they do not fit. Your keyword map becomes a checklist you reference while optimizing to ensure complete coverage.
Avoid keyword stuffing patterns
Google penalizes content that repeats keywords unnaturally. Your target keyword should appear 2 to 4 times per 1,000 words in most cases, though this varies by topic and competition. Focus on using synonyms and related phrases rather than repeating exact match keywords. If you find yourself using the same phrase three times in one paragraph, rewrite those sentences to use natural variations instead.
Step 3. Rewrite for clarity and completeness
Your content now has the right search intent and a solid keyword map. The next step is transforming raw content into clear, complete information that satisfies both readers and ranking algorithms. You need to eliminate ambiguity, fill content gaps, and restructure sentences that slow comprehension. This revision process directly impacts engagement metrics like time on page and bounce rate, which Google uses to evaluate content quality.
Simplify sentence structure and remove fluff
You should target 15 to 20 words per sentence as your average. Scan your content for sentences exceeding 25 words and break them into shorter statements. Long, complex sentences create cognitive load that makes readers abandon your page. Remove filler phrases like "it is important to note that" or "in order to" and replace them with direct statements.
Cut any paragraph that does not serve your page goal. If a section exists only to increase word count, delete it. Readers recognize padding immediately, and Google's algorithms detect when content wanders off topic. Each paragraph should advance the reader toward understanding how to optimize content for SEO or completing a specific action.
Fill information gaps with comprehensive coverage
Compare your content against the top three ranking pages for your target keyword. List every subtopic they cover that your page currently misses. If competitors explain technical concepts your content skips, add those explanations. Your goal is creating the most complete resource available on your topic, not matching competitor length.
Add concrete examples where you currently use abstract explanations. If you state "optimize your meta descriptions," show a before and after example with specific character counts and formatting. Readers trust content that demonstrates concepts rather than just describing them:
Bad: "Make your content engaging"
Good: "Replace passive constructions like 'mistakes were made' with active statements like 'you made three common errors'"
Apply a three-pass editing system
Read your content three separate times, focusing on different elements in each pass. Your first pass checks logical flow between sections. Your second pass verifies that every claim includes supporting evidence or examples. Your third pass eliminates weak verbs and replaces them with specific action words.
Content clarity improves rankings because it reduces the time readers spend searching for answers within your page.
Use readability tools to identify problem areas, but do not write to arbitrary grade levels. Your content should match the complexity of your topic while remaining accessible to your target audience.
Step 4. Optimize on-page elements and media
Your content quality means nothing if technical on-page elements send wrong signals to search engines. You must optimize every visible and invisible component that helps Google understand your page topic and value. This step focuses on the mechanical elements that directly influence how search engines index and rank your content, from title tags to image compression.
Fix your title tags and meta descriptions
Your title tag should include your primary keyword within the first 60 characters while remaining compelling to human readers. Avoid stuffing multiple keywords into titles, as this reduces click-through rates and looks manipulative. Create titles that promise specific value rather than generic claims about quality.
Write meta descriptions between 150 and 160 characters that include your main keyword naturally. Your description should function as advertising copy that convinces searchers to click your result instead of competitors. Include a clear benefit statement or question that matches search intent:
Bad: "Learn about SEO optimization and content tips for better rankings"
Good: "Follow this 6-step checklist to optimize any page for higher Google rankings in 2026"
Optimized title tags and descriptions improve both search rankings and click-through rates from search results.
Optimize images for speed and accessibility
Compress every image to under 100 KB without visible quality loss using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim. Large images destroy page speed, which directly harms rankings. Convert images to WebP format when possible, as it offers better compression than JPEG or PNG while maintaining quality.
Add descriptive alt text to every image that explains what the image shows. Your alt text should help visually impaired users understand image content while incorporating relevant keywords naturally. Avoid keyword stuffing in alt attributes, as this creates accessibility issues and may trigger spam filters.
Structure URLs and headings properly
Create short, keyword-rich URLs that describe page content clearly. Remove stop words like "and," "the," and "of" from URLs to keep them concise. A URL for this guide should be "/how-to-optimize-content-seo" rather than "/the-ultimate-guide-to-learning-how-to-optimize-your-content-for-seo-rankings."
Use only one H1 tag per page, and structure H2 and H3 headings in logical hierarchy. Your headings should outline your content like a table of contents, allowing readers to scan and find specific information quickly. Each heading should include relevant keywords without forcing awkward phrasing just to match search terms exactly.
Step 5. Strengthen links, trust, and UX
Your content needs authority signals and user experience elements that convince both Google and readers that your page deserves trust. Links, citations, and navigation elements work together to create a seamless experience that keeps visitors engaged while building topical authority. You must treat this step as essential to how to optimize content for SEO, not as optional polish you add later.
Add strategic internal links
You should include three to five internal links from each piece of content to related pages on your site. These links help readers discover additional resources while showing Google how your content connects within your broader topical framework. Place internal links within the body text where they naturally support your explanation, not clustered at the end as an afterthought.
Link to cornerstone content that covers foundational concepts your current page assumes readers understand. For example, if you mention keyword research in passing, link to your comprehensive keyword research guide. Use descriptive anchor text that tells readers exactly what they will find when they click, avoiding generic phrases like "click here" or "read more." Your anchor text should match the target page's primary topic.
Build external authority signals
Every factual claim in your content needs supporting evidence from authoritative sources. When you cite statistics, link directly to the original research or data source. Google rewards content that demonstrates research depth by referencing high-quality external sites like official documentation, academic studies, or government databases.
Add outbound links to two or three authoritative sources that support your key points. These signals show Google that you have researched your topic thoroughly rather than making unsupported claims. Choose sources that readers will recognize as trustworthy, which builds confidence in your content's accuracy.
External links to authoritative sources strengthen your content's credibility without diluting your page's ranking potential.
Improve user experience elements
Format your content for easy scanning by adding sufficient white space between paragraphs and using bullet points for lists of related items. Readers should find answers quickly without reading every word. Break dense paragraphs into shorter blocks that mobile users can consume without scrolling endlessly.
Add a clickable table of contents at the top of long articles that lets readers jump directly to sections that interest them. This navigation element reduces frustration and improves engagement metrics by helping visitors find specific information immediately. Your table of contents should use the same heading text that appears in your H2 and H3 tags for consistency.
Step 6. Refresh, measure, and repeat
Optimization does not end when you publish your improved content. You must track performance metrics and refresh your content regularly to maintain rankings and capture new opportunities. Google rewards pages that stay current with updated information, fresh examples, and expanded coverage as topics evolve. Your optimization strategy should include a systematic process for measuring results and making data-driven improvements over time.
Track ranking changes and traffic patterns
You should monitor your target keywords weekly using Google Search Console to identify ranking improvements or drops. Focus on position changes for keywords ranking between positions 5 and 20, as these represent your best opportunities for quick wins with minor content updates. Document which optimization changes you made and when, so you can connect specific actions to ranking movements.
Check your organic traffic trends monthly to spot patterns that indicate content decay or seasonal changes. Look for pages that previously ranked well but have lost 20% or more traffic over three months. These pages need immediate attention through content refreshes. Compare your traffic against competitor rankings to identify when algorithm updates affect your niche rather than just your content quality.
Regular measurement reveals which optimization tactics work for your specific content and audience, letting you double down on successful strategies.
Update content based on performance data
You need to refresh underperforming pages every 90 days by adding new information, updating statistics, and improving sections that receive low engagement. Add current year references to titles and introductions to signal freshness. Replace outdated examples with recent case studies that demonstrate how to optimize content for SEO using current best practices.
Expand sections where readers spend the most time by adding deeper explanations or additional examples. If your analytics show high exit rates on specific sections, rewrite those areas for clarity or add visual elements that improve understanding. Test different calls-to-action and measure which versions drive better conversion rates toward your page goals.
Schedule regular optimization cycles
Create a quarterly review calendar that assigns specific optimization tasks to each content piece on your site. High-value pages should receive updates every three months, while evergreen content can work on six-month cycles. Use this template to organize your optimization schedule:
| Content Type | Review Frequency | Key Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| High-traffic pages | Every 3 months | Update stats, add examples, check competitors |
| Product pages | Every 2 months | Refresh descriptions, update pricing, add reviews |
| Evergreen guides | Every 6 months | Verify accuracy, expand sections, improve media |
Set calendar reminders that trigger your optimization workflow automatically, ensuring pages never become stale through neglect.
Next steps
You now have a complete framework for how to optimize content for SEO that covers everything from search intent validation to ongoing performance tracking. The six-step process you learned here transforms underperforming pages into ranking assets when you apply each step systematically.
Start with your highest-traffic pages that currently rank between positions 5 and 15. These pages already have authority signals and need only minor optimization to reach the first page. Apply the checklist to one page this week, measure results after 30 days, then scale your process to additional content.
Manual optimization works, but it consumes significant time when you manage multiple websites or publish content daily. RankYak automates the entire optimization process, from keyword research through publishing and backlink building, letting you focus on strategy instead of execution. The platform handles technical optimization, content creation, and performance tracking across your entire content portfolio without requiring constant oversight.

Get Google and ChatGPT traffic on autopilot.
Start today and generate your first article within 15 minutes.
