What Is an SEO Strategy? Step-by-Step Guide With Examples
You know SEO matters. You know you need it. But when you sit down to actually improve your rankings, you hit a wall. Should you start with keywords? Fix technical issues? Write more content? Without a clear plan, you end up spinning your wheels and watching competitors climb past you.
An SEO strategy gives you that plan. It's your roadmap for increasing organic traffic through coordinated, purposeful actions that build on each other. Instead of random tactics, you get a system that tells you exactly what to do and when to do it.
This guide walks you through building an SEO strategy from scratch. You'll learn what an SEO strategy actually is, how to audit your current position, find the right keywords, create optimized content, fix technical problems, and measure your progress. We'll include real examples and show you how to adapt these steps to your specific situation. By the end, you'll have a clear framework for getting your pages to rank and driving more qualified visitors to your site.
What an SEO strategy actually is
An SEO strategy is a documented plan for improving your site's rankings and organic traffic over time. It defines which keywords you'll target, what content you'll create, how you'll fix technical issues, and how you'll build authority through backlinks and signals. The key difference between having a strategy and doing random SEO work: you make every decision based on data and clear business priorities, not gut feelings or the latest trend you read about.
The core components that make it work
Your strategy needs to answer several specific questions before you start executing. What pages will you optimize and in what order of priority? Which audience segments will each page serve and what problems will you solve for them? How will you measure success beyond just tracking rankings? A complete strategy includes your target keywords mapped to specific pages, a content calendar that supports your customer funnel, technical fixes prioritized by their impact on rankings, and a practical link building approach that matches your resources and timeline.
You can document this in a spreadsheet, a Google Doc, or project management software. The format matters far less than having it written down, shared with your team, and actually used to guide your daily decisions.
What separates real strategy from random tactics
Many businesses confuse SEO tactics with actual strategy. Writing blog posts is a tactic. Publishing guest articles is a tactic. Running technical audits is a tactic. Your strategy explains why you're doing each of these things and how they connect to measurable business outcomes. It answers critical questions: which topics will drive qualified traffic that converts? How will different content types work together to move prospects through your funnel? What's the realistic timeline for seeing results from each initiative?
Without this strategic thinking, you end up with content that gets traffic but doesn't convert, or technical fixes that take weeks but don't improve rankings.
A strategy without tactics is daydreaming. Tactics without strategy is chaos.
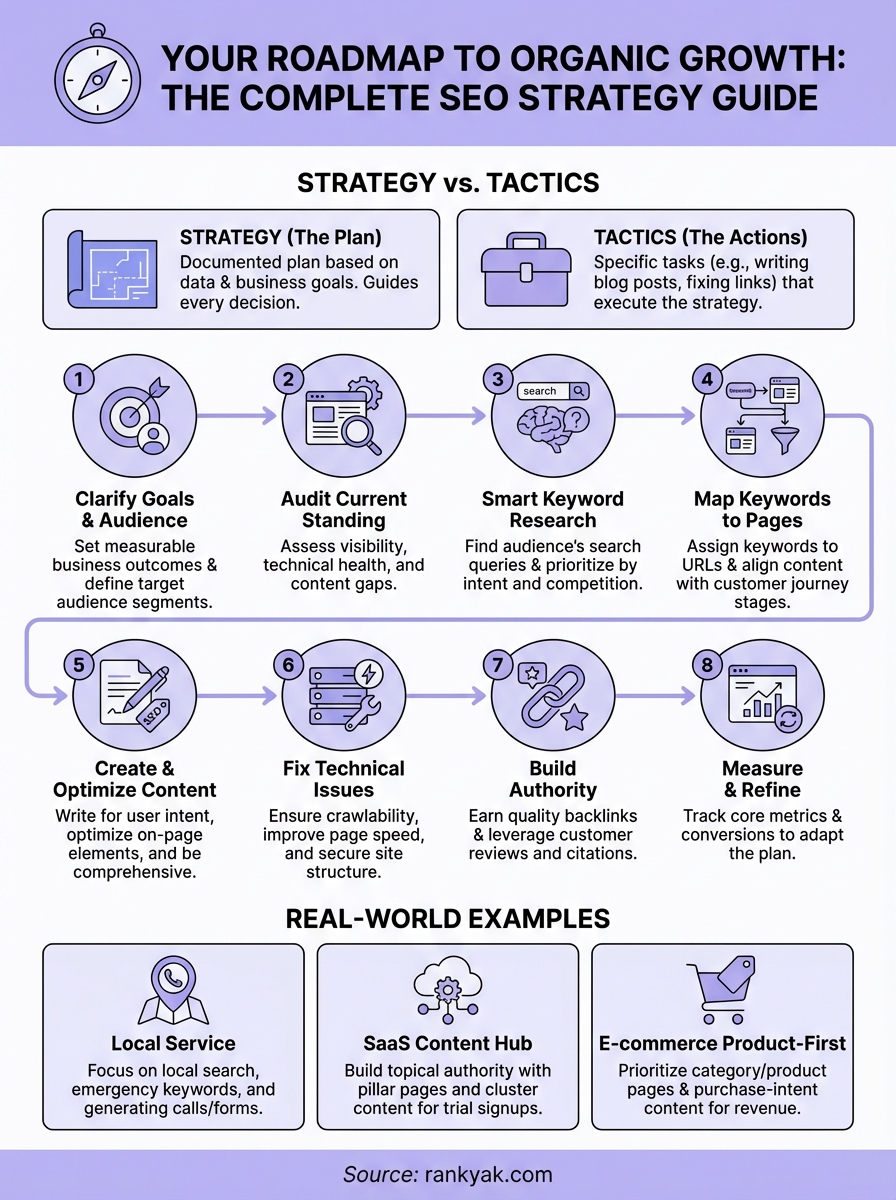
Step 1. Clarify your goals and audience
You can't build an effective strategy without knowing exactly what you're trying to achieve and for whom. Your SEO goals should connect directly to business outcomes, not vanity metrics like "rank #1 for keyword X." Start by identifying whether you need more qualified leads, increased product sales, higher engagement with specific content types, or improved brand visibility in your market. Each goal changes what you'll prioritize in your strategy.
Define measurable business outcomes
Set specific targets tied to revenue or conversions rather than focusing solely on traffic numbers. A local service business might aim for 50 qualified lead form submissions per month from organic search within six months. An e-commerce site could target a 30% increase in organic revenue from product pages over the next quarter. A SaaS company might focus on generating 100 free trial signups per month from educational content.
Document your goals using this framework:
- Primary goal: The main business outcome you need (example: increase organic revenue by $50,000/month)
- Supporting metrics: Traffic increases, ranking improvements, conversion rate changes
- Timeline: Realistic deadline based on your market competition and resources
- Success threshold: Minimum acceptable result that justifies the investment
Your goals will determine everything else in your strategy, from which keywords you target to how you measure success. Without clear outcomes defined upfront, you'll waste time on work that doesn't move your business forward.
Strategy begins with knowing exactly what winning looks like for your specific business.
Identify who you're actually writing for
Your target audience determines which topics you'll cover and how you'll present information. Create specific audience profiles that include their search behavior, problems they're trying to solve, questions they ask, and where they are in the buying journey. A B2B software buyer researching solutions behaves completely differently than a consumer looking for product reviews.
List the key audience segments you need to reach:
- Primary persona: Your ideal customer who drives most revenue
- Search patterns: What phrases they actually type into Google
- Pain points: Specific problems your content will solve
- Content preferences: Whether they want quick answers, deep guides, videos, or comparisons
Understanding what is an SEO strategy means recognizing that different audiences require different content approaches. Your strategy must align what you create with what your specific audience actually searches for and needs.
Step 2. Audit where your SEO stands today
You need to know your starting position before you can build an effective strategy. An SEO audit reveals what's already working, what's broken, and where your biggest opportunities lie. This assessment saves you from wasting time on tactics that won't move the needle and helps you prioritize fixes that will actually improve your rankings. Understanding what is an SEO strategy requires this baseline because you can't measure progress without knowing where you started.

Check your current visibility and performance
Start by gathering data on how Google currently sees and ranks your site. Sign into Google Search Console and review your performance over the past 90 days. Look at which pages get the most impressions and clicks, what your average click-through rate is, and which queries already bring traffic to your site. Export this data to a spreadsheet so you can reference it later when measuring improvement.
Next, identify pages that rank on the second or third page of results (positions 11-30). These pages represent your quickest wins because they already have some authority but need optimization to break into the top 10. Focus your initial efforts here rather than trying to rank brand new content from scratch.
Your fastest SEO gains come from improving pages that already rank just outside the first page of results.
Run a technical health scan
Technical issues block search engines from properly crawling and indexing your content. Use Google Search Console's Coverage report to find pages that aren't being indexed and understand why. Common problems include broken internal links, redirect chains, duplicate content, missing or incorrect robots.txt directives, and slow page load times.
Check these critical technical elements:
- Site speed: Pages that load in under 3 seconds using Google PageSpeed Insights
- Mobile responsiveness: How your site displays and functions on smartphones
- HTTPS security: Whether your entire site uses secure protocols
- XML sitemap: If you have one submitted and if it's error-free
- Structured data: Whether you're using schema markup correctly
Document every issue you find with its current status and potential impact on rankings. This list becomes your technical SEO action plan prioritized by severity and ease of fixing.
Analyze your existing content gaps
Review the content you've already published and compare it against what actually ranks in Google for your target topics. Open an incognito browser window and search for key phrases your audience uses. Study the top 5 results for each query and note what format they use (guides, listicles, videos), how comprehensive they are, and what specific questions they answer.
Identify gaps where you have no content addressing important topics your audience searches for, or where your existing content falls short of what's ranking. These gaps guide your content creation priorities in the next steps of your strategy.
Step 3. Do smart keyword and topic research
Keyword research identifies the exact phrases your target audience types into Google when looking for solutions you provide. This step determines which topics you'll create content around and which terms you'll optimize for. Without proper keyword research, you'll waste time creating content that either nobody searches for or that's impossible to rank for given your site's current authority. Understanding what is an SEO strategy means recognizing that your keyword choices drive every other decision you make.
Start with seed keywords from your business
Begin with terms that directly describe your products, services, or core topics. List 10-20 phrases that your customers use when they talk about what you offer. A project management software company might start with "project management tool," "task tracking software," "team collaboration platform," and "project planning app." An accounting firm could begin with "small business accounting," "tax preparation services," "bookkeeping help," and "financial planning."
Don't filter or optimize these initial terms yet. Your goal is to generate a broad list that represents different ways people might search for what you do. Include industry terminology, common misspellings, and alternative phrases. This seed list becomes the foundation for finding hundreds of related keyword opportunities in the next step.
Find what your audience actually searches for
Take each seed keyword and expand it into related phrases using Google's autocomplete and "People Also Ask" sections. Type your seed keyword into Google and note the suggestions that appear. Scroll through the search results and capture questions from the "People Also Ask" boxes. These suggestions come directly from real user searches and reveal the specific language and questions your audience uses.
Create a spreadsheet with these columns to organize your research:
| Keyword Phrase | Monthly Search Volume | Keyword Difficulty | Search Intent | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| project management software | 12,000 | 78 | Commercial | High |
| free project management tools | 3,600 | 45 | Commercial | High |
| how to manage projects effectively | 2,400 | 32 | Informational | Medium |
Track the search intent for each keyword (informational, commercial, transactional, or navigational) because this determines what type of content you'll need to create. Someone searching "what is project management" needs educational content, while someone searching "best project management software" wants product comparisons.
The keywords you choose define not just your rankings, but the quality and relevance of traffic you'll attract.
Prioritize based on competition and opportunity
Focus on keywords where you can realistically compete given your site's current authority. Look for phrases with decent search volume (at least 100-500 monthly searches for most businesses) but lower competition scores (under 40-50 on most keyword difficulty scales). Target longer, more specific phrases like "project management software for construction companies" rather than broad terms like "project management" when you're building initial traction.
Prioritize keywords that align with your business goals from Step 1. If you need qualified leads, focus on commercial intent keywords. If you're building brand awareness, informational keywords work better. Select 20-30 primary keywords you'll target in the next quarter, organized by priority and estimated effort required to rank.
Step 4. Map keywords to pages and funnels
Assign each keyword to a specific page or piece of content you'll create. This mapping prevents cannibalization (where multiple pages compete for the same keyword) and ensures every search query has a clear destination on your site. Without this step, you'll create redundant content that confuses both search engines and users. Understanding what is an SEO strategy includes recognizing that strategic keyword assignment determines whether your content works together or against itself.
Create your keyword-to-page mapping
Build a spreadsheet that connects each target keyword to exactly one URL on your site. List your primary keywords in one column, the target URL in another, and the page type (homepage, service page, blog post, product page) in a third. If a keyword doesn't have a matching page yet, mark it as "content to create" and add it to your content calendar.
Here's a practical template for your mapping:
| Target Keyword | Assigned URL | Page Type | Funnel Stage | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| project management software | /product | Product page | Decision | Existing |
| how to manage remote teams | /blog/manage-remote-teams | Blog post | Awareness | To create |
| project management tool comparison | /compare | Comparison page | Consideration | To create |
| project management pricing | /pricing | Pricing page | Decision | Existing |
Review this mapping monthly and adjust as you create new content or identify better keyword opportunities. Your mapping document becomes the central reference that guides all content decisions and prevents wasted effort.
Align content with funnel stages
Match each keyword to where prospects are in their buying journey. Awareness stage keywords (informational searches like "what is project management") need educational blog posts that build trust. Consideration stage keywords (commercial searches like "best project management tools") require comparison guides and feature explanations. Decision stage keywords (transactional searches like "buy project management software") connect to product pages, pricing pages, and case studies.
Create distinct content for each funnel stage:
- Top of funnel (Awareness): Educational guides, how-to articles, problem-focused content
- Middle of funnel (Consideration): Product comparisons, feature breakdowns, use case studies
- Bottom of funnel (Decision): Pricing pages, product demos, customer testimonials, ROI calculators
Your keyword mapping must reflect your customer's journey, not just search volume numbers.
Build topical clusters around pillar pages
Organize your keyword mapping into topic clusters where one comprehensive pillar page covers a broad topic and multiple supporting posts address specific subtopics. A pillar page about "project management" might link to cluster content about "project planning," "team collaboration," "project tracking," and "project reporting." Each cluster post targets long-tail keywords while strengthening the pillar page's authority.
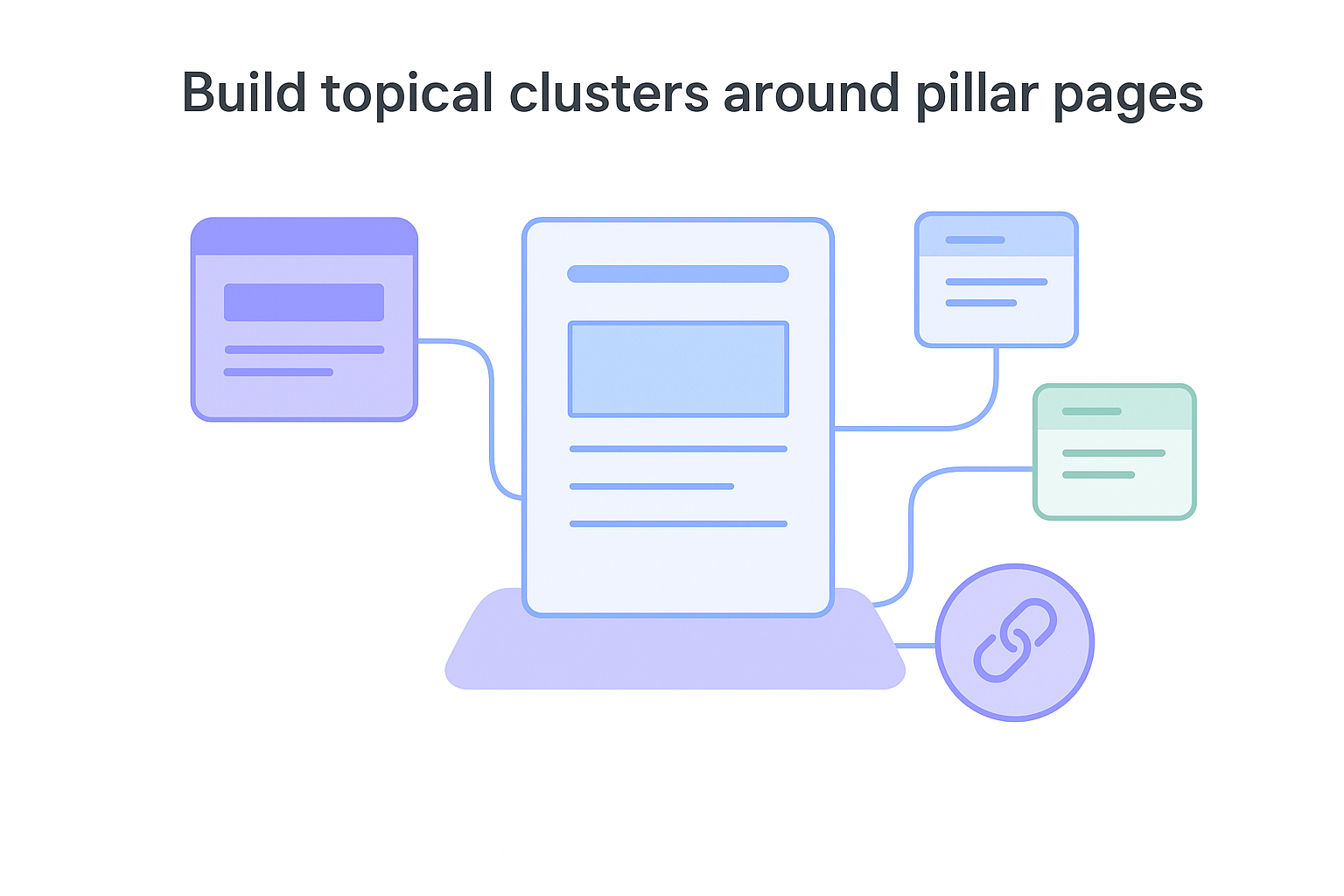
Use internal links to connect cluster content back to your pillar page and between related cluster posts. This structure helps search engines understand your topic expertise and improves rankings across your entire cluster. Plan 1-3 pillar pages initially, each with 5-10 cluster posts, before expanding to additional topics.
Step 5. Create and optimize SEO content
Creating content that ranks requires matching both user intent and Google's quality standards. You need to write content that genuinely helps your audience while incorporating the optimization elements that search engines use to evaluate and rank pages. Your content must be better than what currently ranks for your target keywords, or you're simply adding to the noise. This step turns your keyword research and mapping into actual pages that drive traffic and conversions.
Write content that matches search intent
Study the top 5 results for your target keyword before you write a single word. Open each page and analyze what format they use (guide, listicle, comparison, how-to), how long they are, what specific questions they answer, and what makes them valuable to readers. If the top results are all 2,000-word comprehensive guides, your 500-word post won't compete. If they're all product comparisons with tables and pricing, writing a general overview misses the mark.
Create an outline that covers all the subtopics appearing across top-ranking pages, then add unique value through your expertise:
- Original examples from your experience
- Data or case studies competitors haven't shared
- Clearer explanations of complex concepts
- More current information that updates outdated content
- Different perspectives that challenge conventional wisdom
Match the search intent exactly. When someone searches "how to create a project plan," they want step-by-step instructions, not a product pitch. When they search "best project management software," they want comparisons and recommendations, not a tutorial on project planning methodology. Understanding what is an SEO strategy includes recognizing that intent alignment determines whether your content ranks.
Content that perfectly matches search intent will always outrank content that doesn't, regardless of other optimization factors.
Optimize your on-page elements
Place your target keyword in specific locations where it carries the most weight for search engines. Include it naturally in your title tag, H1 heading, URL slug, first paragraph, at least one H2 subheading, and meta description. Don't force it into every paragraph or it reads awkwardly and triggers spam filters.
Here's a practical template for optimizing a blog post targeting "project management tips":
URL: /blog/project-management-tips
Title Tag: 15 Project Management Tips That Actually Work [2026]
Meta Description: Discover proven project management tips from industry experts. Learn practical strategies to keep projects on track and teams productive.
H1: Project Management Tips That Transform Team Performance
First paragraph: "These project management tips come from managing over 200 projects..."
H2 examples: "Communication Tips for Project Managers" | "Planning Tips That Prevent Delays"
Use related keywords and synonyms naturally throughout your content rather than repeating the exact phrase. Google understands that "project management strategies," "PM techniques," and "managing projects effectively" all relate to your main topic.
Make your content comprehensive and structured
Break your content into clear sections with descriptive headings that help both readers and search engines understand your structure. Use H2s for main sections and H3s for subsections. Add bullet points to make lists scannable, include tables to compare options or present data, and use bold text to highlight key takeaways in each paragraph.
Aim for these content standards based on competition analysis:
- Word count: Match or exceed the average length of top 3 results by 20-30%
- Images: Include 3-5 relevant visuals (screenshots, diagrams, charts)
- Internal links: Add 3-5 links to related content on your site
- External links: Reference 2-3 authoritative sources when citing data or claims
Write for humans first, then optimize for search engines. Your content needs to actually answer questions and solve problems, not just rank. Include examples, templates, and actionable steps that readers can implement immediately.
Step 6. Fix technical SEO and site structure
Technical problems stop search engines from properly crawling, indexing, and ranking your content. Even perfectly written content won't rank if Google's bots can't access it or if your pages load too slowly. You need to identify and fix these issues systematically before they undermine your entire strategy. Technical SEO creates the foundation that allows your content and keyword optimization to actually work.
Audit your site's crawlability and indexing
Check Google Search Console's Coverage report to see which pages Google has successfully indexed and which ones it's having trouble with. Look for errors like "Crawled - currently not indexed," "Discovered - currently not indexed," or "Excluded by 'noindex' tag." These issues prevent your content from appearing in search results no matter how well optimized it is.
Run this basic crawlability checklist:
- Robots.txt file: Verify you're not accidentally blocking important pages
- XML sitemap: Ensure it's submitted and contains all your priority pages
- Redirect chains: Fix any URLs that redirect multiple times before reaching the final destination
- Broken links: Repair or remove internal links pointing to 404 pages
- Duplicate content: Use canonical tags to specify the preferred version when similar content exists
Update your robots.txt file to allow crawling of important sections while blocking low-value pages like admin areas or search result pages. Here's a basic template:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /search/
Sitemap: https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml
Technical SEO problems act as invisible barriers between your content and rankings, no matter how good your content is.
Improve page speed and Core Web Vitals
Test your site speed using Google PageSpeed Insights and focus on fixing the issues it identifies as highest priority. Slow pages frustrate users and rank lower than faster competitors. Your goal is to achieve loading times under 3 seconds on both mobile and desktop devices.

Implement these speed improvements in order of impact:
- Compress images: Use WebP format and keep file sizes under 200KB
- Enable browser caching: Set expiration dates for static resources
- Minify CSS and JavaScript: Remove unnecessary code and whitespace
- Use a content delivery network (CDN): Serve content from servers closer to your users
- Lazy load images: Load images only as users scroll to them
Pay special attention to Core Web Vitals (Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift) because Google uses these metrics as ranking factors. These measurements focus on real user experience rather than just technical performance.
Structure your site for easy navigation
Organize your pages into a clear hierarchy where users can reach any page within 3-4 clicks from your homepage. Use descriptive category structures in your URLs that reflect your site's organization. A good structure looks like /category/subcategory/page-name rather than /page?id=12345.
Create this navigation structure:
- Homepage links to main category pages
- Category pages link to subcategories and individual content pages
- Individual pages link back to their parent category and related content
- Footer navigation provides quick access to important pages
Build internal links between related pages using descriptive anchor text that includes relevant keywords. Understanding what is an seo strategy means recognizing that your internal linking structure helps search engines understand which pages are most important and how topics connect across your site.
Step 7. Build authority with links and reviews
Backlinks and reviews signal to search engines that your site deserves trust and credibility. You need other websites to reference your content and real customers to vouch for your business. These external signals carry significant weight in Google's ranking algorithm because they represent third-party validation that your site provides value. Without authority signals, your well-optimized content competes at a disadvantage against established sites.
Get backlinks from relevant websites
Focus on earning links from sites in your industry or related topics rather than chasing any backlink you can get. A single link from a reputable industry publication carries more weight than dozens of links from random directories or low-quality blogs. Reach out to sites that have linked to similar content or that would genuinely benefit their audience by referencing your resources.
Create outreach emails that offer specific value rather than generic requests:
Subject: Resource for your [article title] post
Hi [Name],
I noticed your article on [topic] at [URL]. You mentioned [specific point from their article].
I recently published a comprehensive guide on [related topic] that includes [unique value proposition]. It might be a helpful resource to add to your article, especially the section on [specific relevant section].
Here's the link: [your URL]
Either way, great article!
[Your name]
Target 5-10 high-quality backlink opportunities per month from guest posts, resource page additions, broken link replacements, or journalist requests through platforms like HARO (Help a Reporter Out). Quality matters far more than quantity when building your link profile.
Authority built through genuine relationships and valuable content compounds over time, while shortcuts lead to penalties.
Leverage customer reviews and testimonials
Actively request reviews from satisfied customers on Google Business Profile, industry-specific review sites, and your own website. Reviews improve your local search rankings and increase click-through rates from search results by displaying star ratings. Understanding what is an seo strategy includes recognizing that user-generated content like reviews provides fresh, relevant signals that search engines value.
Implement this review generation system:
- Send review requests 3-7 days after purchase or service completion
- Make the process easy with direct links to your review profiles
- Respond to all reviews, both positive and negative
- Display reviews prominently on relevant product or service pages
- Use schema markup to help search engines display star ratings in search results
Build local citations for local businesses
List your business on relevant directories with consistent NAP information (Name, Address, Phone number) across all platforms. Inconsistent information confuses search engines and weakens your local authority. Submit your business to Google Business Profile first, then add listings to industry-specific directories, local chambers of commerce, and established directories like Yelp and Bing Places.
Verify that every listing includes your exact business name, full address, phone number, website URL, business hours, and category. Check existing citations quarterly to ensure accuracy as your business information changes.
Step 8. Measure results and refine your plan
Track specific metrics that connect to your business goals rather than obsessing over rankings alone. You need to know which pages drive conversions, which keywords bring qualified traffic, and where visitors drop off in your funnel. Measurement turns your SEO strategy from guesswork into a systematic process where you double down on what works and fix what doesn't. Understanding what is an seo strategy includes recognizing that the execution phase requires constant monitoring and adjustment based on real performance data.
Track your core SEO metrics weekly
Review these essential metrics in Google Search Console and Google Analytics every week to catch trends early and respond quickly to ranking changes. Focus on metrics that indicate both visibility and engagement rather than vanity numbers that don't impact revenue.
Monitor these performance indicators consistently:
| Metric | Tool | What It Tells You | Target Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic sessions | Google Analytics | Total traffic from search | Steady increase |
| Impressions | Search Console | How often your pages appear in search | Growing visibility |
| Click-through rate | Search Console | Percentage who click when they see you | Above 3% average |
| Average position | Search Console | Where you rank for target keywords | Moving toward positions 1-5 |
| Pages per session | Google Analytics | Content engagement depth | Above 2 pages |
| Conversion rate | Google Analytics | Percentage who complete goal actions | Improving or stable |
Export this data monthly and compare it to your baseline from Step 2 to measure concrete progress against your original goals. Look for patterns like which days of the week drive the most traffic or which content types keep visitors engaged longest.
Set up conversion tracking beyond rankings
Define what conversion means for your business and configure Google Analytics to track these specific actions. Rankings mean nothing if visitors don't take the next step you want them to take. Set up goal tracking for form submissions, product purchases, email signups, phone calls, chat initiations, or video plays depending on what drives your business forward.
Create a monthly dashboard that connects SEO metrics to business outcomes. Track organic revenue if you run an e-commerce site, qualified leads if you offer services, or demo requests if you sell software. This dashboard proves SEO's value to stakeholders and helps you prioritize which pages and keywords deserve more investment.
Measuring conversions transforms SEO from a traffic game into a revenue driver that justifies continued investment.
Refine based on what the data shows
Analyze underperforming content monthly and decide whether to improve it, consolidate it with related pages, or remove it entirely. Look at pages with high impressions but low click-through rates and rewrite their title tags and meta descriptions to be more compelling. Find pages ranking in positions 8-15 and add more comprehensive information, better examples, and stronger internal links to push them into the top 5 results.
Adjust your content calendar based on which topics drive the most engagement and conversions. If product comparison articles convert better than educational guides, shift more resources toward creating comparison content. When certain keywords prove too competitive given your current authority, pivot to related long-tail variations where you can win faster.
SEO strategy examples you can model
Real examples show you how to translate strategy concepts into practical action plans. These three examples demonstrate how different businesses structure their SEO strategies based on their goals, resources, and target audiences. You can adapt these frameworks to your specific situation by replacing their keywords and pages with ones relevant to your business. Understanding what is an seo strategy becomes clearer when you see how actual companies organize their efforts.
Local service business strategy
A plumbing company in Austin targets local customers who need immediate help with specific problems. They focus their entire strategy on local search terms and emergency service keywords because that matches how their customers actually search. Their primary goals center on generating phone calls and form submissions from people ready to hire someone today.
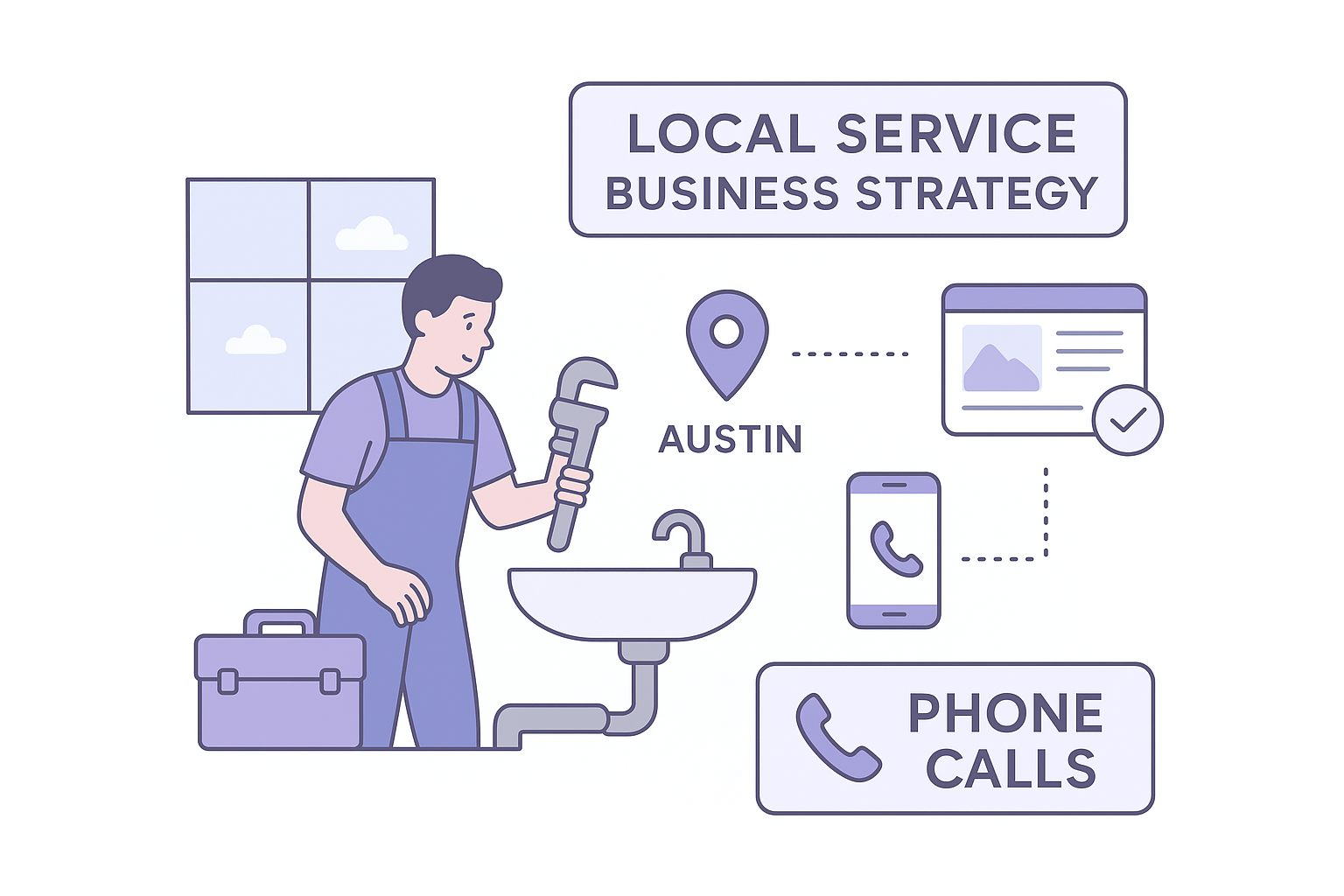
Their quarterly action plan looks like this:
| Priority | Action | Target Keywords | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Optimize Google Business Profile | N/A | Week 1 |
| 2 | Create service area pages | "plumber in [neighborhood]" | Weeks 2-4 |
| 3 | Publish problem-solving guides | "how to fix [specific issue]" | Ongoing weekly |
| 4 | Get customer reviews | N/A | Ongoing |
| 5 | Build local citations | N/A | Month 2 |
Each piece connects directly to their conversion goal of booking service calls. They measure success by tracking phone calls from organic search and form submissions attributed to specific landing pages.
Strategy works when every tactic connects to a measurable business outcome, not just traffic numbers.
SaaS company content hub strategy
A project management software company builds topical authority around their core use cases. They create pillar pages for each major feature or benefit, then surround those pages with 8-12 supporting blog posts that target long-tail variations. Their goal focuses on generating free trial signups from people actively researching solutions.
This company organizes their content in clusters:
Pillar page: "/features/task-management" (targets: "task management software")
Cluster posts:
- "How to prioritize tasks effectively" (informational, top of funnel)
- "Task management for remote teams" (informational, middle funnel)
- "Best task management software for agencies" (commercial, bottom funnel)
- "Task management vs project management" (commercial, middle funnel)
They link every cluster post back to the pillar page and between related posts. This structure builds authority for competitive commercial keywords while capturing informational searches that introduce prospects to their solution earlier in the buying journey.
E-commerce store product-focused strategy
An outdoor gear retailer prioritizes product pages and buying guide content that directly drives purchases. They invest most resources in optimizing category pages, individual product pages, and comparison content because these pages convert browsers into buyers. Traffic to informational blog posts matters less than organic revenue from product pages.
Their optimization priority list ranks pages this way:
- Category pages for broad product types ("hiking boots," "camping tents")
- Product pages for bestselling items with review schema markup
- Comparison guides for high-consideration purchases ("best winter sleeping bags")
- Buying guides that link to multiple related products
- How-to content only when it naturally promotes product usage
They track organic revenue per landing page and double down on optimizing pages that already convert. Product pages get rich snippets through structured data, detailed specifications, customer photos, and FAQ sections that answer common pre-purchase questions.
Next steps for your SEO strategy
Start with the audit and keyword research steps outlined in this guide rather than jumping directly into content creation. You now understand what is an SEO strategy and how to build one that drives measurable results, but success requires consistent execution over weeks and months. Pick your top 5-10 priority keywords from Step 3 and map them to specific pages you'll create or optimize in the next 30 days.
Document your strategy in a simple spreadsheet that your entire team can access and update. Block time weekly to review your performance metrics and adjust your approach based on what actually moves your rankings and conversions. Most businesses see initial ranking improvements within 60-90 days when they execute systematically.
If you want to skip the manual work of keyword research, content creation, and publishing, RankYak automates your entire SEO strategy by generating optimized articles daily and handling everything from keyword discovery to backlink building.

Get Google and ChatGPT traffic on autopilot.
Start today and generate your first article within 15 minutes.
