On-Page SEO Factors: 12 Essentials to Rank High in 2026
You publish content but your pages sit buried on page three or four of Google. You know SEO matters but every article you read throws dozens of on-page SEO factors at you without explaining which ones actually move your rankings. You waste hours tweaking elements that barely make a difference while missing the factors that could push you to page one.
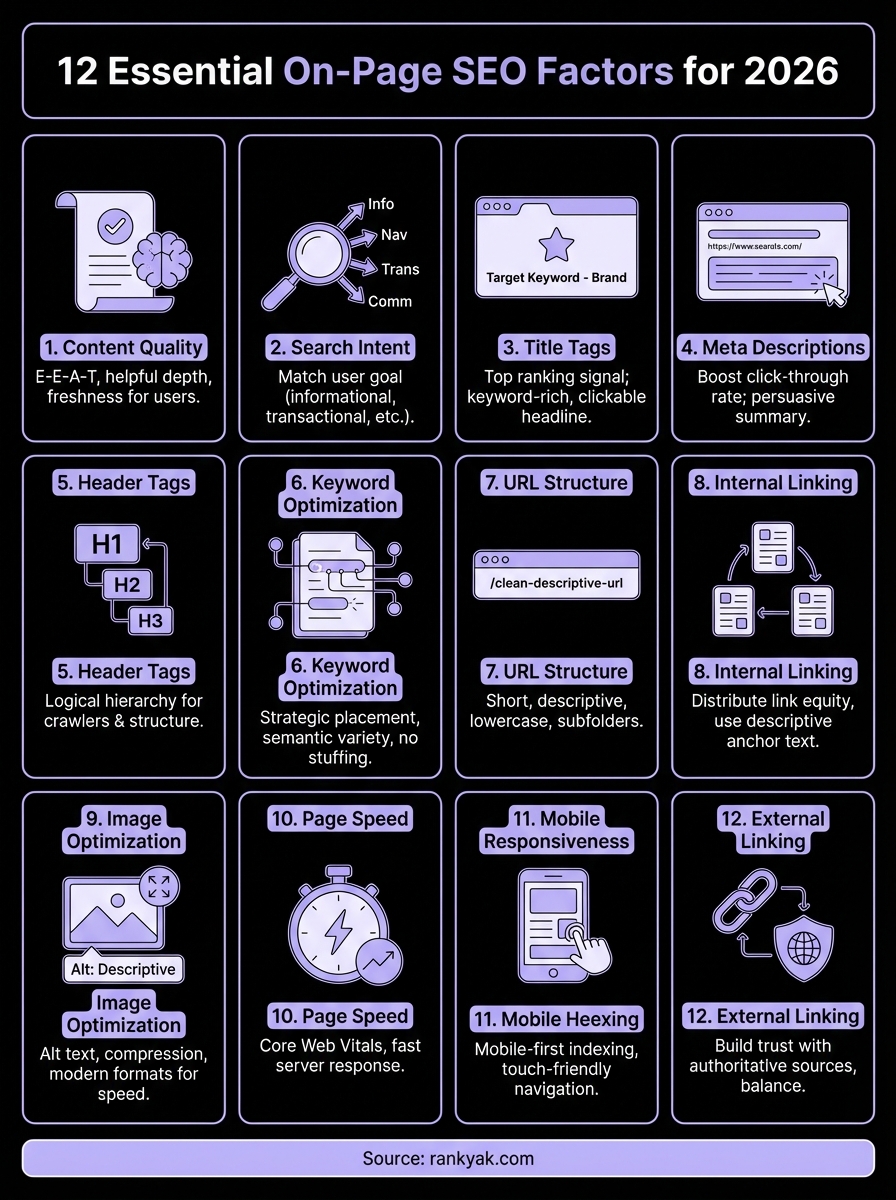
This guide breaks down 12 essential on-page elements that directly impact your rankings in 2026. You'll learn what each factor does, why it matters, and exactly how to optimize it on your pages. Each section gives you actionable steps you can apply today to start climbing the search results. No fluff. Just the on-page optimizations that get your content ranking.
1. Content quality
Content quality sits at the top of on-page SEO factors because Google's algorithms now evaluate how well your pages actually help readers. Your content needs to demonstrate expertise, answer questions thoroughly, and provide information people trust. Search engines measure quality through multiple signals including time on page, bounce rate, and how often other sites reference your work.
Understanding E-E-A-T and helpful content
Google judges content based on Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). You need to show first-hand knowledge of your topic, whether that means using a product, visiting a location, or working in the field. Pages that simply rewrite information from other sources without adding original insights or personal experience rank lower. Your content should make readers feel they learned something valuable they couldn't find elsewhere.
Search engines also prioritize content created for people, not algorithms. You satisfy this by writing to help your audience first and optimizing for search second. Ask yourself if someone landing directly on your page would find it useful, or if they'd immediately search again for better information.
Why content depth beats word count
Comprehensive coverage of a topic matters more than hitting arbitrary word counts. Your page should answer the reader's main question plus related questions they haven't thought to ask yet. This means including relevant subtopics, addressing common objections, and providing context that rounds out their understanding.
Deep content keeps readers engaged and signals to search engines that your page deserves higher rankings.
Shallow pages that repeat the same points or pad content with filler get filtered out. Focus on substance over length by covering all angles of your topic without redundancy.
The role of content freshness
Regular updates tell search engines your page remains relevant and accurate. You don't need to rewrite everything, but you should review content periodically to add new information, fix outdated references, and expand sections that need more detail. Industries change, products evolve, and reader questions shift over time.
Fresh content also gives you opportunities to improve underperforming pages. Check which sections get the most engagement and expand those areas. Update statistics, add recent examples, and remove information that no longer applies to keep your content current and valuable.
2. Search intent
Search intent determines whether your content matches what users actually want when they type a query. You can optimize every other on-page SEO factor perfectly but still rank poorly if your page doesn't satisfy the searcher's goal. Google analyzes user behavior to understand if your content type, depth, and format align with what people expect to find. Pages that deliver on intent earn higher rankings because users engage with them instead of bouncing back to search results.
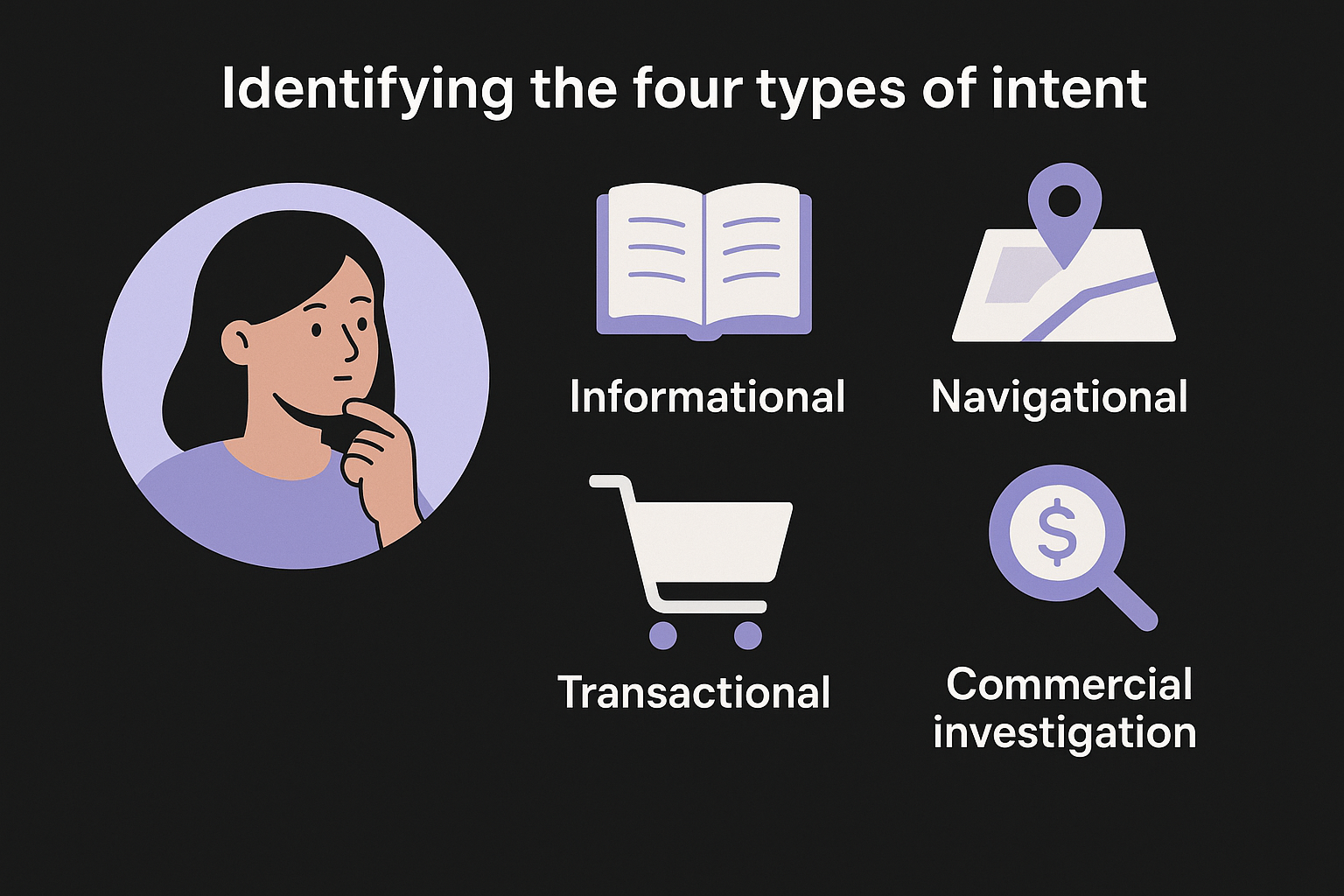
Identifying the four types of intent
Search queries fall into four main categories: informational (learning about a topic), navigational (finding a specific site), transactional (ready to buy), and commercial investigation (researching before purchase). Your content format must match the dominant intent for your target keyword. Informational queries need guides or explanations, navigational searchers want your homepage or specific page, transactional users expect product pages with clear buying options, and commercial queries demand comparisons or reviews.
Matching content format to user needs
Each intent type requires a different content structure. Informational content works as blog posts, tutorials, or definitions that explain concepts thoroughly. Commercial investigation queries perform best with comparison tables, feature lists, or review roundups that help decision-making. Transactional pages need product descriptions, pricing, and prominent calls to action. Your page format should mirror what currently ranks for your keyword.
Aligning your content type with search intent gives you a direct path to first-page rankings.
Analyzing the SERP for intent clues
Google's search results page reveals what format ranks for your keyword. Look at the top ten results to identify patterns in content type, length, and structure. Video results indicate visual content works well, featured snippets show opportunities for list or table formats, and image packs suggest visual elements matter. Study these patterns to shape your content strategy and match what Google already rewards.
3. Title tags
Title tags function as the clickable headline in search results and tell both users and search engines what your page covers. Google uses your title tag as a primary ranking signal to determine relevance for search queries. Your title also affects click-through rates because it creates the first impression searchers see when your page appears in results. Strong titles combine target keywords with compelling language that makes people want to click.
Why title tags are the top ranking signal
Google analyzes title tags to understand your page topic and match it with relevant searches. Your title carries more ranking weight than most other on-page SEO factors because it directly states what your content delivers. Pages with titles that closely match search queries earn better positions in results. The title tag also appears in browser tabs and when people share your page on social platforms, making it a crucial element for both SEO and user experience.
Best practices for title length and keywords
Place your most important keyword near the beginning of your title where it gets maximum weight. Keep titles between 50-60 characters to ensure they display fully on most devices. Include your brand name at the end if you have room, separated by a vertical bar or dash. Write titles that read naturally for humans while incorporating keywords strategically, avoiding repetition or keyword stuffing that makes titles awkward.
Titles that balance keyword optimization with readability drive both rankings and clicks.
Avoiding title truncation in search results
Search engines cut off titles that exceed their display limits, typically around 600 pixels wide. You lose control of your messaging when Google rewrites long titles or adds ellipses. Preview how your title appears by checking its pixel width in title tag tools or simply keeping it under 60 characters. Front-load the most critical information so even if truncation happens, your core message remains visible to searchers.
4. Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions appear below your title tag in search results and give searchers a preview of your page content. While Google doesn't use meta descriptions as a direct ranking factor, they significantly influence whether people click your result over competitors. Your description serves as ad copy that convinces searchers your page has the answer they need. Well-written descriptions boost click-through rates, which sends positive engagement signals that can improve your position over time.
Impact of descriptions on click-through rate
Your meta description creates the second impression after your title tag, working together to earn clicks. Users scan descriptions quickly to verify your page matches their search intent before deciding to visit. Pages with clear, specific descriptions that preview the value inside earn more clicks than vague or missing descriptions. Higher click-through rates tell search engines your result satisfies searchers better than competing pages, which can gradually improve your rankings as one of the important on-page SEO factors.
Writing persuasive summaries
Effective descriptions summarize your content in 150-160 characters while highlighting the main benefit readers gain. Focus on what makes your page unique or valuable compared to other results on the page. Include your target keyword naturally since Google bolds matching terms in search results, making your description more visible. Write descriptions that directly address the searcher's question or need rather than generic statements about your site.
Descriptions that promise specific value drive more clicks than generic page summaries.
Using active voice and calls to action
Active voice makes descriptions more direct and engaging than passive constructions. Start with action verbs like "Learn," "Discover," or "Find" that tell readers exactly what they'll do on your page. Add subtle calls to action that encourage clicks without sounding pushy, such as "See the full list" or "Get the complete guide." Your description should create urgency or curiosity that makes waiting to click feel like missing out on valuable information.
5. Header tags
Header tags organize your content into a clear structure that both readers and search engines can follow. These HTML elements (H1, H2, H3, etc.) create a visual hierarchy that breaks your page into scannable sections while helping Google understand which topics matter most. Your headers act as signposts that guide visitors through your content and signal topical relevance to search algorithms. Proper header structure ranks among critical on-page SEO factors because it improves user experience and helps crawlers index your content accurately.
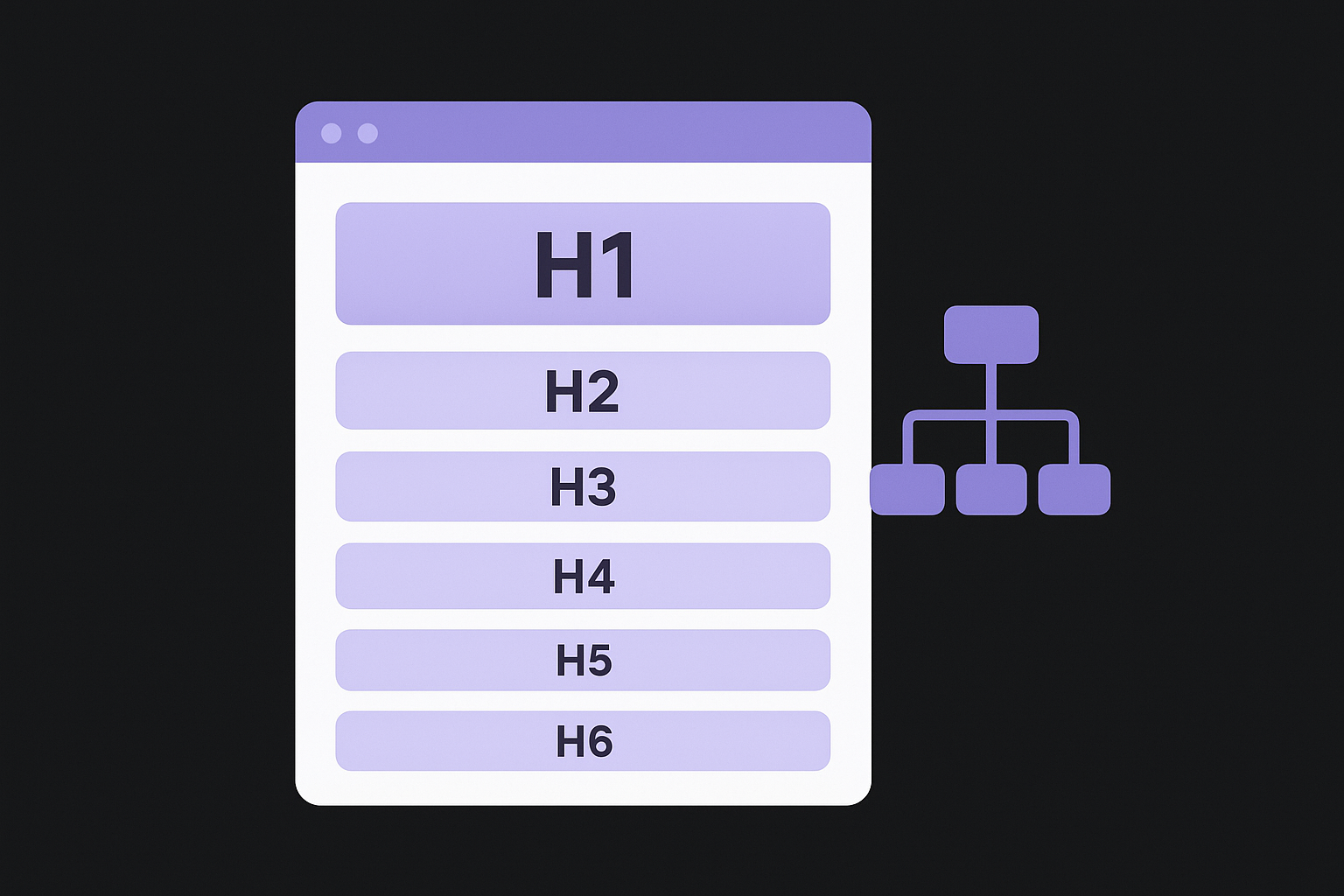
Creating a logical hierarchy with H1-H6
Your page should have exactly one H1 tag that states your main topic, typically matching or closely resembling your title tag. Below that, H2 tags divide your content into major sections, while H3 through H6 tags create subsections within those larger topics. This nested structure mirrors how you'd outline a document, with each level becoming more specific. Search engines expect this logical flow, so skipping levels (jumping from H2 to H4) or using multiple H1s confuses crawlers and weakens your page's topical clarity.
Helping crawlers understand page structure
Search engine bots scan your headers to build a content map of your page and determine what each section covers. Headers that include relevant keywords help crawlers connect your content to search queries. Your header hierarchy also tells Google which topics deserve the most weight when evaluating your page. Well-structured headers make it easier for search engines to extract and display your content in rich results, giving you better visibility in search results.
Headers that clearly outline your content help both users and search engines navigate your page efficiently.
Optimizing headers for featured snippets
Featured snippets often pull content from pages with clear header structures that organize information into digestible sections. You increase your chances of earning these coveted positions by formatting headers as questions that match common searches in your niche. Use H2 or H3 tags to introduce lists, steps, or definitions that answer specific queries. Google favors pages where headers preview the exact information that follows, making it easy to extract and display in snippet format.
6. Keyword optimization
Keyword optimization remains one of the fundamental on-page SEO factors but the strategy has evolved beyond simple repetition. You need to incorporate keywords naturally while covering related concepts and topical depth that search engines expect. Modern algorithms analyze how thoroughly you cover a subject rather than counting keyword mentions. Your focus should shift to providing complete answers that use your target keyword and variations in ways that feel natural to readers.
Moving beyond keyword stuffing
Search engines penalize pages that force keywords unnaturally or repeat them excessively throughout the content. You build better rankings by using your target keyword strategically in key locations while writing primarily for human readers. Include your main keyword in your introduction, conclusion, and a few natural spots throughout your content where it fits the context. The goal is to signal relevance without sacrificing readability or creating awkward sentences that clearly exist just for SEO.
Using semantic keywords and entities
Google understands related terms and concepts that connect to your main keyword through semantic relationships. You strengthen your page's topical authority by including synonyms, related phrases, and entity mentions that naturally belong in a comprehensive discussion of your subject. For example, a page about "on-page SEO factors" should mention terms like "meta tags," "content optimization," and "site structure" without forcing them. These semantic connections help search engines verify you've covered the topic thoroughly.
Pages that incorporate semantic variations rank better than those that repeat exact-match keywords.
Placing keywords in strategic zones
Your keyword carries more ranking weight in specific page locations like your title tag, first paragraph, and headers. Place your main keyword near the beginning of your content where it establishes topic relevance immediately. Use variations in H2 and H3 headers to reinforce what each section covers. Include your keyword in your URL, meta description, and image alt text where it fits naturally without forcing it into every possible spot.
7. URL structure
Your URL structure directly impacts how search engines and users understand your page before they even visit it. Clean, descriptive URLs rank better than messy ones filled with random characters or lengthy parameters. Search engines use your URL as a ranking signal to determine relevance, while users decide whether to click based on how trustworthy your URL appears. Well-structured URLs serve as one of the most straightforward on-page SEO factors you can optimize because they take minutes to fix but improve both rankings and click-through rates.
Keeping URLs short and descriptive
Short URLs perform better in search results because they display fully without truncation and clearly communicate what the page covers. You should keep URLs under 60 characters when possible, using only the essential words that describe your content. Include your target keyword in the URL but avoid stuffing multiple keywords or creating unnecessarily long paths. Descriptive URLs like "/on-page-seo-factors" work better than generic strings like "/page?id=12345" because both users and crawlers immediately understand what they'll find on the page.
Avoiding special characters and dates
URLs with special characters, underscores, or dates create problems for search engines and age your content unnecessarily. Stick to lowercase letters, hyphens, and numbers in your URL structure to ensure maximum compatibility across platforms. Remove dates from URLs because they make evergreen content appear outdated even after you update it, and they create the need for redirects when you refresh content. Characters like %, &, or @ confuse crawlers and look suspicious to users, reducing your click-through rate and making URLs harder to share.
URLs that stay simple and timeless maintain their ranking power as your content evolves.
Organizing content with subfolders
Logical subfolder structures help search engines understand how your content relates to broader topic categories on your site. You can organize pages into folders like "/blog/seo/" or "/guides/marketing/" to create clear topical hierarchies. This organization distributes ranking strength across related pages and helps users navigate your site more intuitively. Keep folder depth under three levels to maintain simple, accessible URLs that don't dilute your page authority through excessive nesting.
8. Internal linking
Internal linking connects your pages together to help search engines discover content and understand how your site's information relates. These links pass ranking power between pages while guiding visitors to relevant content they might find useful. Strategic internal linking ranks among the most underutilized on-page SEO factors because it requires ongoing attention as you publish new content. Your internal link structure tells crawlers which pages matter most while creating pathways that keep readers engaged and exploring your site.
Distributing link equity across pages
Every page on your site carries ranking strength that you can share with other pages through internal links. You strengthen underperforming pages by linking to them from your highest-authority content, passing some of that page's link equity to help newer or weaker pages rank better. Focus your internal links on pages you want to rank rather than spreading links randomly across your site. Your most important pages should receive more internal links from throughout your site, signaling their significance to search algorithms.
Using descriptive anchor text
Anchor text tells search engines what the linked page covers, so generic phrases like "click here" waste valuable optimization opportunities. You should use descriptive phrases that include relevant keywords or clearly describe the destination content. Vary your anchor text across different links to the same page instead of repeating identical phrases that look manipulative. Natural anchor text flows within your sentences while giving readers and crawlers a clear preview of what they'll find when they click.
Internal links with descriptive anchor text guide both users and search engines to your most valuable content.
Building topic clusters
Topic clusters organize your content into hub pages that cover broad subjects, surrounded by detailed articles that explore specific aspects. You create these clusters by linking related articles to each other and back to the main hub page, establishing topical authority in your niche. This structure helps search engines recognize you as an expert on the topic while making it easier for readers to find comprehensive information. Strong topic clusters improve your rankings for competitive keywords by demonstrating depth across the entire subject area.
9. Image optimization
Image optimization affects page speed, accessibility, and search visibility, making it a crucial element among on-page SEO factors. Search engines can't "see" images the way humans do, so they rely on text signals like file names, alt text, and surrounding content to understand what your images show. Properly optimized images load faster, improve user experience, and give you opportunities to rank in image search results. Your images should enhance your content without slowing down your pages or creating accessibility barriers.
Writing descriptive alt text for accessibility
Alt text describes your images to screen readers and search engines when images fail to load. You should write specific descriptions that explain what the image contains rather than stuffing keywords unnaturally. Include your target keyword in alt text only when it accurately describes the image content. Screen reader users depend on alt text to understand visual content, so vague descriptions like "image1" or leaving alt text empty creates accessibility problems and wastes SEO value.
Compressing images for faster load times
Large image files slow your page speed and hurt rankings across all devices. You need to compress images before uploading them to reduce file size without destroying visual quality. Modern compression tools can shrink images by 50-80% while maintaining clarity that looks identical to visitors. Balance image quality with file size by testing different compression levels to find the smallest file that still looks sharp on your pages.
Compressed images improve page speed while delivering the same visual impact to your visitors.
Using modern file formats
WebP and AVIF formats deliver better compression ratios than traditional JPEG and PNG files. These newer formats reduce file sizes by 25-35% compared to older formats while maintaining the same image quality. Most modern browsers support WebP, making it a safe choice for faster loading images that don't sacrifice visual appeal.
10. Page speed
Page speed measures how quickly your content loads and becomes interactive for visitors. Slow pages frustrate users and push them back to search results, which tanks your rankings. Google treats speed as a ranking factor and prioritizes fast-loading pages in search results because they deliver better user experiences. Your page speed affects every visitor regardless of device, making it one of the most impactful on-page SEO factors you can optimize for immediate results.
Understanding Core Web Vitals
Google evaluates your page speed through Core Web Vitals, three specific metrics that measure loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) tracks how fast your main content loads, First Input Delay (FID) measures how quickly your page responds to interactions, and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) monitors unexpected layout changes that frustrate users. Your pages should meet Google's thresholds for all three metrics to avoid ranking penalties and provide smooth experiences.

Reducing server response time
Your server needs to deliver page content within 200 milliseconds to avoid speed bottlenecks. You reduce server response time by upgrading hosting infrastructure, implementing caching systems, and optimizing database queries that slow down content delivery. Slow servers delay everything else on your page regardless of how well you optimize other elements.
Handling JavaScript and CSS execution
JavaScript and CSS files block page rendering when they load synchronously, creating delays before users see your content. You speed up rendering by deferring non-critical JavaScript, minifying CSS files, and removing unused code that adds weight without value. Inline critical CSS directly in your HTML to render above-the-fold content immediately while loading the rest asynchronously.
Fast pages that execute code efficiently keep visitors engaged and signal quality to search algorithms.
11. Mobile responsiveness
Mobile responsiveness determines how well your pages function on smartphones and tablets, which now account for the majority of web traffic. Google switched to mobile-first indexing, meaning it evaluates your mobile version first when deciding rankings. Your pages need to deliver the same content quality and functionality on mobile devices as they do on desktop, or you risk losing rankings across all searches. Mobile responsiveness sits among critical on-page SEO factors because poor mobile experiences push visitors away and tell search engines your pages don't meet user needs.
Adapting to mobile-first indexing
Google's crawlers now use your mobile version as the primary source for indexing and ranking your content. You need to ensure your mobile pages contain the same text, images, and structured data as your desktop version. Pages that hide content on mobile or serve stripped-down versions lose ranking power because Google can't find the signals it needs to evaluate your page properly. Your mobile layout should present all essential content without requiring horizontal scrolling or zooming.
Ensuring touch-friendly navigation
Mobile users interact with your pages through touch gestures rather than mouse clicks, requiring larger tap targets and adequate spacing between links. You should maintain minimum 44x44 pixel touch targets for buttons and links to prevent mis-taps that frustrate visitors. Navigation menus need to expand easily on mobile screens without overlapping content or creating accidental clicks.
Touch-optimized pages keep mobile visitors engaged instead of sending them back to search results.
Testing responsiveness across devices
Your pages must function correctly across different screen sizes and orientations without breaking layouts or hiding content. You test responsiveness by checking your pages on actual mobile devices or using browser developer tools to simulate various screen dimensions. Pay attention to how images scale, whether text remains readable without zooming, and if forms work properly on smaller screens.
12. External linking
External linking connects your content to relevant sources outside your site, building credibility and context for both readers and search engines. Linking to high-quality external sources demonstrates you've researched your topic thoroughly and aren't afraid to reference other experts. While external links don't directly boost your rankings like internal links do, they function as trust signals that improve how search engines evaluate your content as one of the important on-page SEO factors. Your outbound links show you're creating content to genuinely help readers rather than keeping them trapped on your site.
Building trust with authoritative sources
You strengthen your content's credibility by citing authoritative websites like government agencies, educational institutions, and established organizations in your field. Search engines evaluate the quality of sites you link to as part of their trust assessment of your page. Links to sketchy or low-quality sites can hurt your credibility, while connections to respected sources reinforce that you're providing accurate, well-researched information. Reference sources that support your claims or provide additional depth readers might want to explore beyond what your page covers.
Balancing outbound links
Your pages should include external links where they add value without overdoing it to the point of sending readers away too quickly. You strike the right balance by linking to sources that expand on points you mention briefly or back up statistics and claims with original research. Avoid excessive outbound linking that makes your content feel like a directory rather than a substantive resource.
External links that enhance your content build trust without diluting your page's value.
Handling broken external links
Broken outbound links create poor user experiences and suggest your content hasn't been maintained. You should check external links periodically and update or remove ones that lead to 404 errors or irrelevant redirected pages. Regular link audits keep your content functional and show search engines you maintain your pages actively.
Start ranking higher today
You now have the complete on-page SEO factors checklist that determines where your pages rank in search results. These twelve elements work together to signal relevance, build trust, and deliver the user experience Google rewards. Implementation separates pages that climb to page one from those stuck in obscurity. Each factor you optimize compounds with the others to create stronger ranking signals.
Optimizing all these factors manually takes hundreds of hours you probably don't have. RankYak handles the entire process automatically, from keyword research to publishing fully optimized articles that incorporate every factor you've learned here. Your pages get published daily with proper structure, mobile responsiveness, internal linking, and all the technical elements search engines demand. Start your 3-day free trial and watch your rankings climb without touching a single meta tag or title yourself.

Get Google and ChatGPT traffic on autopilot.
Start today and generate your first article within 15 minutes.
